Page 63 - SAMENA Trends - January 2020
P. 63
ARTICLE SAMENA TRENDS
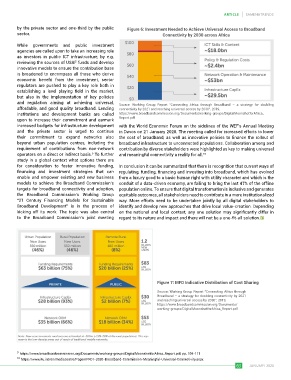
by the private sector and one-third by the public Figure 6: Investment Needed to Achieve Universal Access to Broadband
sector. Connectivity by 2030 across Africa
While governments and public investment
agencies are called upon to take an increasing role
as investors in public ICT infrastructure, by e.g.
reviewing the sources of USAF funds and develop
innovative models to ensure the contribution base
is broadened to encompass all those who derive
economic benefit from the investment, sector
regulators are pushed to play a key role both in
establishing a level playing field in the market,
but also in the implementation of key policies
and regulation aiming at achieving universal, Source: Working Group Report “Connecting Africa through Broadband – a strategy for doubling
affordable, and good quality broadband. Lending connectivity by 2021 and reaching universal access by 2030”, 2019,
institutions and development banks are called https://www.broadbandcommission.org/Documents/working-groups/DigitalMoonshotforAfrica_
upon to increase their commitment and earmark Report.pdf
increased budgets for infrastructure development with the World Economic Forum on the sidelines of the WEF’s Annual Meeting
and the private sector is urged to continue in Davos on 21 January 2020. The meeting called for increased efforts to lower
their commitment to expand networks also the cost of broadband, as well as innovative policies to finance the rollout of
beyond urban population centres, including the broadband infrastructure to unconnected populations. Collaboration among and
requirement of contributions from non-network contribution by diverse stakeholders were highlighted as key to making universal
9
operators on a direct or indirect basis. To further and meaningful connectivity a reality for all. 10
study in a global context what options there are
for consideration to foster innovative funding, In conclusion it can be summarized that there is recognition that current ways of
financing and investment strategies that can regulating, funding, financing and investing into broadband, which has evolved
enable and empower existing and new business from a luxury good to a basic human right with utility character and which is the
models to achieve the Broadband Commission’s conduit of a data-driven economy, are failing to bring the last 47% of the offline
targets for broadband connectivity and adoption, population online. To ensure that digital transformation is inclusive and generates
the Broadband Commission’s Working Group equitable outcomes, all stakeholders need to contribute in a more institutionalized
“21 Century Financing Models for Sustainable way. More efforts need to be undertaken jointly by all digital stakeholders to
Broadband Development” is in the process of identify and develop new approaches that drive local value-creation. Depending
kicking off its work. The topic was also central on the national and local context, any one solution may significantly differ in
to the Broadband Commission’s joint meeting regard to its nature and impact and there will not be a one-fit-all solution.
Figure 7: MFD Indicative Distribution of Cost Sharing
Source: Working Group Report “Connecting Africa through
Broadband – a strategy for doubling connectivity by 2021
and reaching universal access by 2030”, 2019,
https://www.broadbandcommission.org/Documents/
working-groups/DigitalMoonshotforAfrica_Report.pdf
9 https://www.broadbandcommission.org/Documents/working-groups/DigitalMoonshotforAfrica_Report.pdf, pp. 109-111
10 https://www.itu.int/en/mediacentre/Pages/PR01-2020-Broadband-Commission-Meaningful-Universal-Connectivity.aspx
63 JANUARY 2020